Case study in ML: Property assessment in Cook County
Lecture 2
Cornell University
INFO 4940/5940 - Fall 2025
August 28, 2025
Announcements
Announcements
If you’re on the waitlist, wait for a PIN from the Bowers CIS registrar
At present, everyone on the waitlist should be able to get in
If you cannot access Posit Workbench yet, let me know
For grad students, also consider INFO 5940 (Building LLM Applications)
Learning objectives
- Assess competing interests in defining the objectives of a predictive model
- Evaluate the impact of model decisions on stakeholders
- Identify potential sources of bias in a predictive model
- Describe the role of transparency in model development
Results of student questionnaire
What do you hope to learn from this class?
- How ML is used in practice (MLOps cycle)
- Utilizing LLMs effectively
- Learn R/improve coding skills for machine learning
- How to prepare for a career in data science
What are you most excited about doing in this course?
- RAGs (Retrieval-Augmented Generation)
- Customizing LLMs for projects (e.g. RAGs, fine-tuning, prompt design)
- Building tools and interactive applications
- Hands-on projects
- More practice collecting and cleaning data
- Model deployment
What are you most concerned about doing in this course?
- Limited programming experience (especially in R)
- Limited ML background
- R vs. Python
- Project expectations
- General uncertainty
What do you think is currently missing?
- Agentic AI and advanced architectures
- More readings and theory behind models (particularly LLMs)
- Ethics in ML
- Smaller applied assignments for hands-on practice
- Option to complete projects individually
Planned adjustments
- More frequent (but smaller) homework assignments to practice implementing techniques
- Homework 0 to practice Quarto, Positron, and course infrastructure
- Clearly distinguish readings assigned to everyone vs. readings specific to Python or R
Property assessment in the United States
Tax collections in the United States
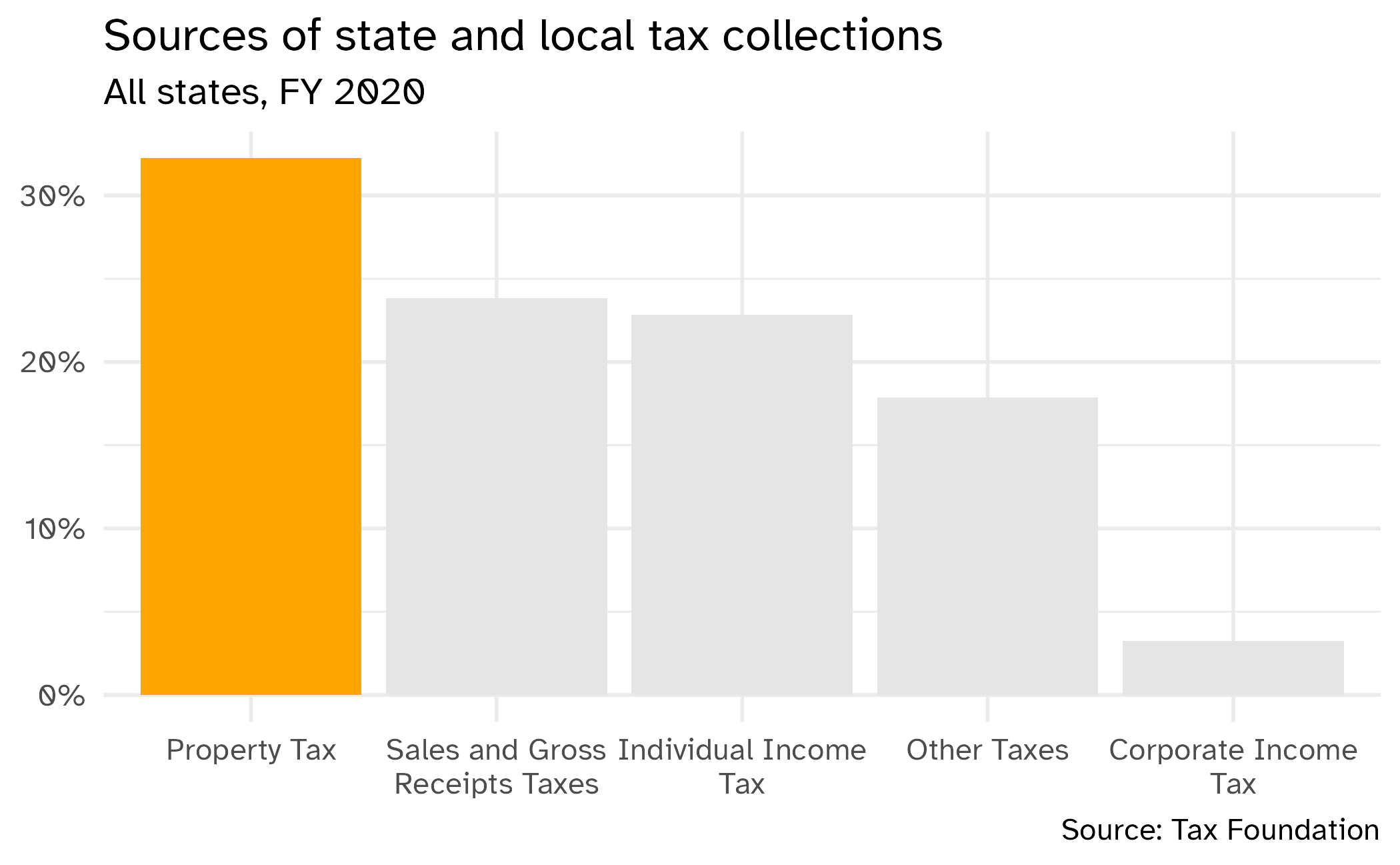
Data source: Tax Foundation
Determining property tax rates
Determining property assessments
Who decides?
- Often a local tax assessor’s office
- Assessors can be elected or appointed (varies by jurisdiction)
How do they decide?
🤷♀️
- Typically for residential properties, use a market approach
- What would the property sell for on the open market?
- Approaches to generating these predictions vary widely
Regressive tax system
- Property tax system only works if properties are assessed accurately
- Inaccurate assessments can lead to regressive tax systems
Sales ratio in Tompkins County, NY
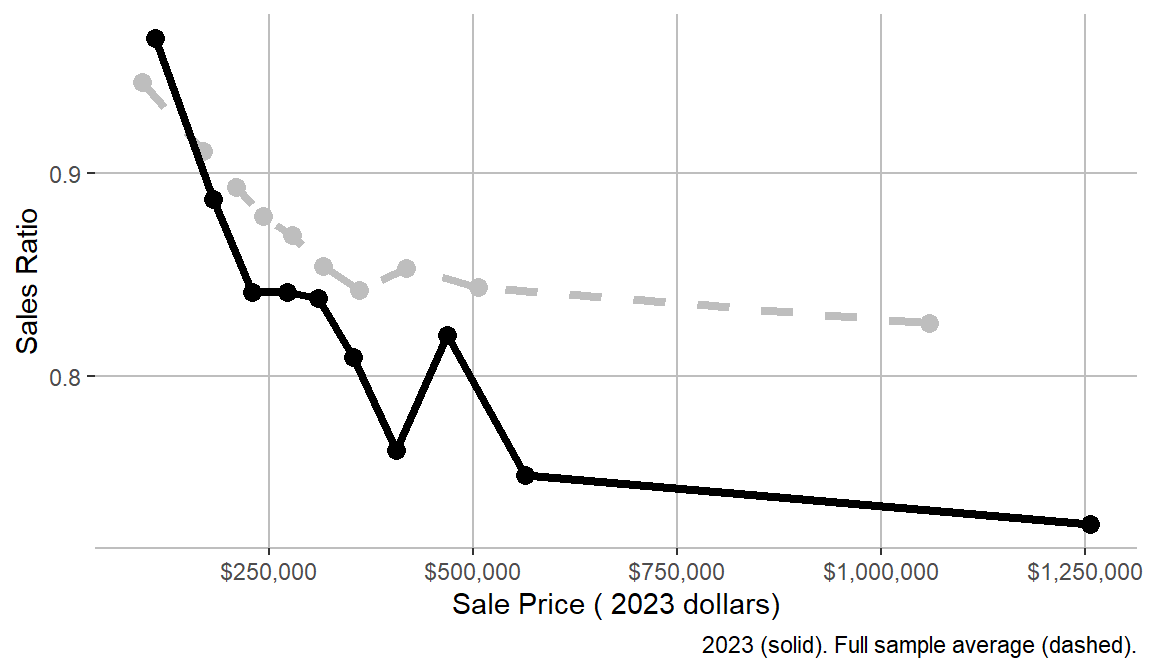
Illustration credit: Center for Municipal Finance
Property assessment in Cook County
- Historically regressive and corrupt
- Residential properties overvalued
- Commercial properties undervalued
- Shifts the tax burden onto homeowners (often lower-income)

Sales ratio over time in Cook County, IL
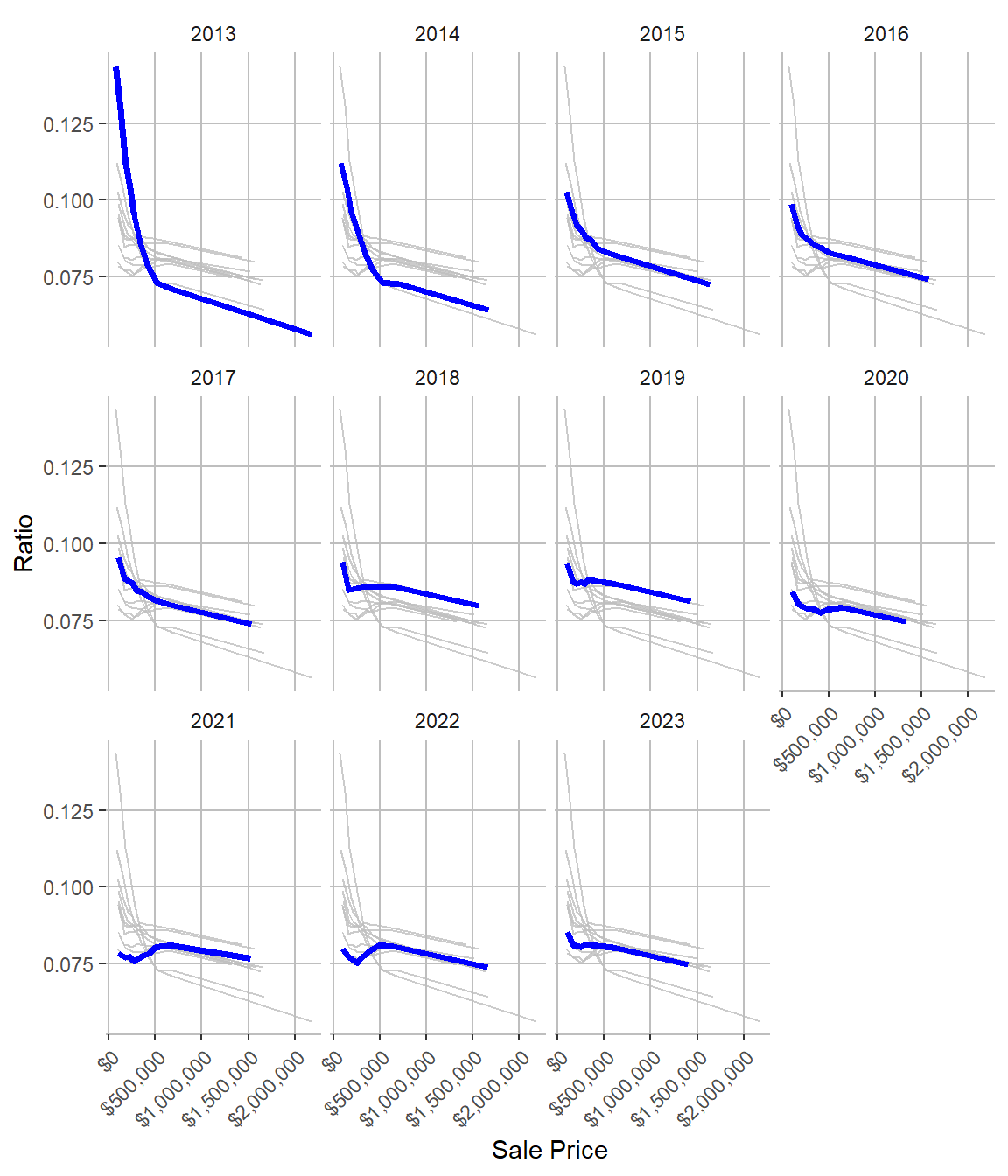
Illustration credit: Center for Municipal Finance
Predictive modeling for property assessment
100 day initiatives and objectives
- 2018 - Fritz Kaegi elected as Cook County Assessor
- 100 Day Initiatives and Objectives
- Improve assessment methodologies
- Openness and transparency
- Update IT infrastructure
- Leads to new residential assessment model
Extremely brief recap of the model
What would the sale price of every Cook County home be if it had sold last year?
- Estimates the sale price of unsold properties using known sale price of similar and nearby properties
- Incorporates both property characteristics and geographic/environmental/market trend variables
- Employs a LightGBM model to generate predictions
Initiating a machine learning project
Stakeholders
| Role | Responsibilities |
|---|---|
| Project sponsor | Represents the business interests; champions the project |
| Client | Represents end users’ interests; domain expert |
| Data scientist | Sets and executes analytic strategy; communicates with sponsor and client |
| Impacted users | Those impacted by the project; whom decisions are made about |
📝 Identify the stakeholders
Instructions
Who is the sponsor for the Cook County Assessor’s Office project? Who is the client? Impacted users? What might be their competing goals/interests?
Record your answers on the provided worksheet. We will collect them at the end of class for your application exercise credit.
08:00
Choices made
- Model selection
- Features used
- Data sources
- Selection of training/assessment data
📝 Trade-offs in project development
Instructions
Pick a choice that the office made in developing their assessment model. What are the trade-offs of this choice versus other options they could have taken? How might this choice impact different stakeholders?
08:00
Evaluating potential bias in a model
- Reporting bias
- Historical bias
- Selection bias
- Confirmation bias
📖 Additional reading: Fairness: Types of bias
📝 Evaluating potential bias in a model
Instructions
Identify one type of bias that you think would impact the property assessment model. How might you evaluate this bias? What steps could you take to mitigate it?
- Reporting bias
- Historical bias
- Selection bias
- Confirmation bias
08:00
Transparency and accountability: A study in contrasts
Cook County, IL
- Publishes entire model on GitHub
- Includes all data files + code to reproduce
- Describes in detail key model choices
Tompkins County, NY
- No transparency on how assessments are generated
- Data is inaccessible to the public
- Most data that is published is only released as a PDF 😒
- To their credit, they do publish annual reports documenting efforts to improve equity in assessments
- Annual complaints from the public about new assessments
📝 Change the system in Tompkins County
Instructions
If Tompkins County were to adopt an approach similar to Cook County, what might be the benefits and drawbacks? What issues would still remain?
08:00
Wrap-up
Recap
- Property assessments are a critical part of the tax system in the United States
- The Cook County Assessor’s Office has made strides in improving their assessment model
- Transparency and accountability are key to building trust in the model